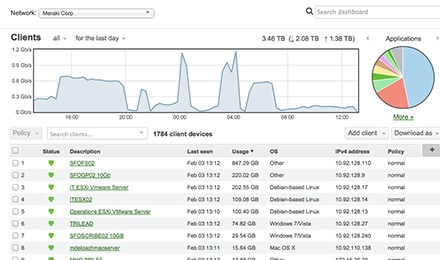
Software-defined WAN is a new approach to network connectivity that lowers operational costs and improves resource usage for multi-site deployments, allowing network administrators to use bandwidth more efficiently and ensure the highest possible level of performance for critical applications without sacrificing security or data privacy. For more information on deploying and configuring SD-WAN on the Meraki MX Security Appliance, see the Meraki SD-WAN Deployment Guide.
Application Optimisation
♦ Centralised next-gen-firewall with network visibility and control.
♦ QoS and bandwidth management with application-QoS and traffic shaping.
Transport Independence
♦ Easy-to-configure IPsec overlay using Meraki Auto VPN.
♦ Traffic distribution over multiple pathways (Internet, cellular, MPLS) with built-in load balancing and automatic fail over capabilities.
Intelligent Path Control
♦ Policy-based routing: Traffic path assigned based on source, destination, or application.
♦ Dynamic path selection: Traffic path chosen per-application based on loss, latency, and jitter.
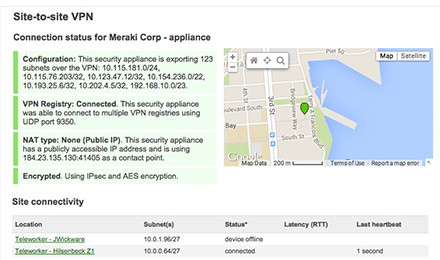
Secure Connectivity
♦ Intuitive, scaleable VPN solution to connect remote sites with ease (Auto VPN).
♦ AES encryption to ensure data privacy.
Why choose SD-WAN?
Today, IT departments are under pressure to do more with less: manage more sites and more clients with limited budgets and a relatively small team, all without any reduction in reliability and security. The high cost of enterprise WAN connectivity, support, and personnel combined with the growth of bandwidth-hungry streaming applications and cloud-based services, is forcing many network admins to search for alternative solutions.
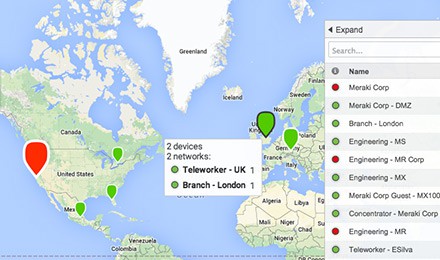
With SD-WAN, remote sites are connected over low-cost Internet links secured by VPN. MPLS-like reliability is provided through multiple uplinks with load balancing capabilities, intelligent path control, and automatic fail over.

SD-WAN Features
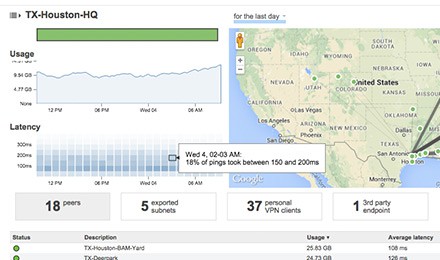
Dual-Active VPN Uplinks
In addition to supporting dual WAN uplinks and automatic VPN failover, the MX also has the ability to build multiple VPN tunnels that are active simultaneously on both uplinks, whether they are Internet or MPLS connections. Traffic can then be load-balanced across these tunnels to make optimal use of available bandwidth.
Policy Based Routing (PBR)
PBR functionality allows administrators to assign traffic to a particular VPN path based on criteria such as traffic protocol, source, destination, or application.
Dynamic Path Selection
Dynamic path selection allows administrators to set performance thresholds for different types of traffic, in order to ensure that critical applications and data transfers always use the best path based on the loss, latency, and jitter over the available VPN tunnels.
CASE STUDY - Deep Dive: Penn Mutual saves $858k
Goals
♦ Implement a BYOD platform at 50 remote sites.
♦ Reduce management and connectivity costs.
Solution
♦ Complete Meraki hardware stack: MX, MS, MR.
♦ Broadband connectivity at branch locations.
Business Outcomes
♦ Reduced Telco spend by 40%.
♦ Improved IT efficiency with a unified management platforms.
Projected 3-Year Cost
with Legacy WAN Development
| Connectivity T1 × 45 at branches (1.544Mbps each) Broadband × 2 at HQ & DR (45Mbps each) |
$2,016,000 $582,000/yr $90,000/yr |
| Content Management Content filtering software |
$153,000 $51,000/yr |
| Maintenance Hardware Security Appliance |
$24,750 $8,250/yr |
| 3 Year Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) | $2,193,750 |
Projected 3-Year Cost
with Meraki (including RIP and Replace)
| Connectivity Broadband × 38 at HQ & branches (50Mbps each) WAN Management Vendor (one-time installation costs) |
$673,495 $212,040/yr $37,375 |
| Meraki Hardware & Licensing MX, MS, and MR × 41 at branches MX, MS, and MR licensing |
$599,141 $382,896 $72,081/yr |
| Content Management | Included |
| Wireless Installation 26 branch offices wired for MR |
$62,257 |
| 3 Year Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) | $1,334,893 |